The Future of Green Construction: Innovations, Regulations, and Market Trends
A Comprehensive Analysis of the Impact of Green Construction Technologies, Regulatory Incentives, and Emerging Market Opportunities in the United States
Introduction
Green construction is becoming increasingly vital in today's world, driven by the urgent need to address environmental challenges while promoting economic efficiency and social well-being. This blog will explore the quantitative benefits of green construction, provide updates on US regulations shaping the industry, and highlight key technological innovations and the startups pioneering these advancements. By understanding these elements, stakeholders can better navigate and capitalize on the opportunities within the evolving green construction landscape.
Green construction technology refers to innovative methods and materials used in building and infrastructure projects to reduce environmental impact, enhance energy efficiency, and promote sustainability.
Investing in green construction technology offers compelling opportunities but also presents certain challenges. On the positive side, the global green building market is projected to reach $498 billion by 2024, driven by increasing demand for sustainable solutions. Energy-efficient buildings can reduce operational costs by up to 30% and increase property values by 7%. Moreover, government incentives like infrastructure bills, tax credits and rebates can further reduce investment costs. However, investors must consider the high initial costs, technological uncertainty, and potential market volatility. The payback period for these technologies can be long, affecting short-term profitability.
Importance of Green Construction: Quantitative Analysis
US Regulatory Incentives for Green Construction
US Regulatory Updates in Green Construction
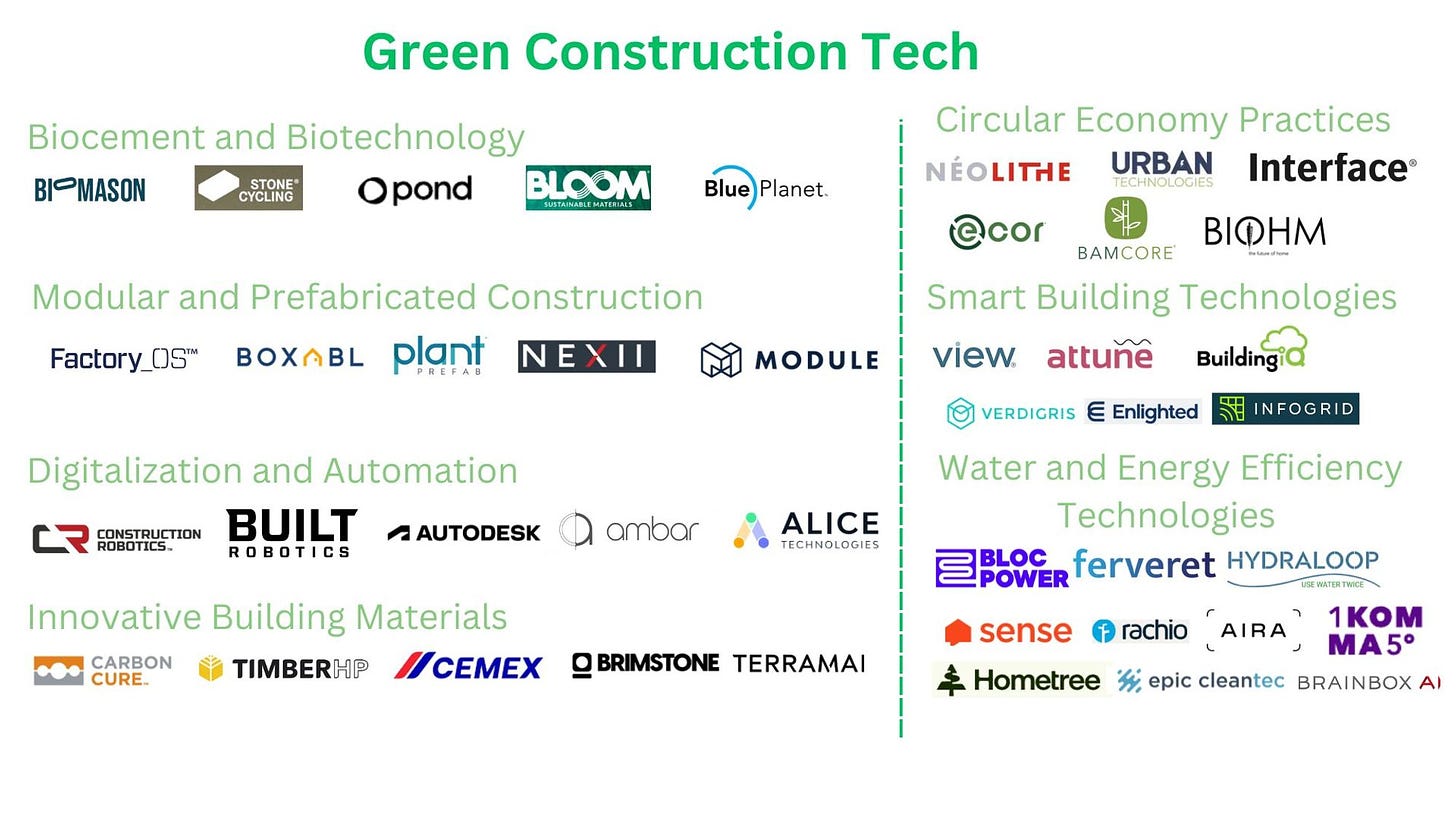
Technological Innovations in Green Construction
Figure 1: Green Construction Tech Mapping by Clarice Qiu
Summary:
The future of green construction technology will focus on net-zero and carbon-negative buildings, which rely on energy-efficient designs, renewable energy, and carbon-sequestering materials like biocement and cross-laminated timber. These buildings will connect with smart grids, enabling dynamic energy management through integration with distributed energy resources (DERs), helping balance energy supply and demand.
3D printing and modular construction will continue to streamline building processes, reducing material waste and labor costs while enabling more efficient designs. Smart buildings, powered by IoT and AI, will optimize energy use in real-time. In addition, liquid cooling systems—already transforming data centers—are poised to enhance energy efficiency in HVAC and other building systems by significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional air cooling methods. As buildings interact with advanced grid infrastructure, including grid-vehicle connections and renewable energy integration, they will contribute to greater grid stability and efficiency.
Additionally, autonomous construction robots, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and water conservation technologies will further boost building sustainability. Government regulations, such as Building Performance Standards (BPS), will continue driving higher efficiency, supported by digital tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and digital twins.