Circuit of Renewal: Transforming the Lifecycle of Lithium Batteries
Exploring Uses, Challenges, and Innovations in Battery Recycling
Introduction
In our rapidly advancing world, lithium batteries have become the backbone of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, as we increasingly rely on these powerful energy sources, it's crucial to address the environmental and economic challenges posed by their disposal. This blog explores the intricacies of lithium-ion batteries, underscoring the importance of recycling, the hurdles it faces, regulatory landscapes, and the emerging innovations shaping the future of battery reuse.
Investing in a lithium battery recycling startups offer both promising prospects and notable challenges. The growing demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions increases the need for recycled materials, potentially making the market for lithium battery recycling both lucrative and environmentally beneficial, supported by various governmental incentives. However, the sector demands substantial initial investment in advanced recycling technology and skilled operations. Additionally, it involves navigating complex technical processes for efficient material recovery and adhering to stringent, often evolving, regulatory frameworks that can significantly impact business operations.
Figure 1: Lithium Ion Battery Recycling [1]
Lithium Batteries and Their Usage
Typical Components of a Lithium-ion Battery
PESTLE Analysis of Lithium-ion Battery Recycling
Regulatory Requirements for Lithium Battery Recycling
Incentives for Lithium Battery Recycling
Why the Recycling Rate of Lithium-ion Battery is Low?
Common Lithium Battery Recycling Methods
Emerging Trends in Lithium Battery Recycling
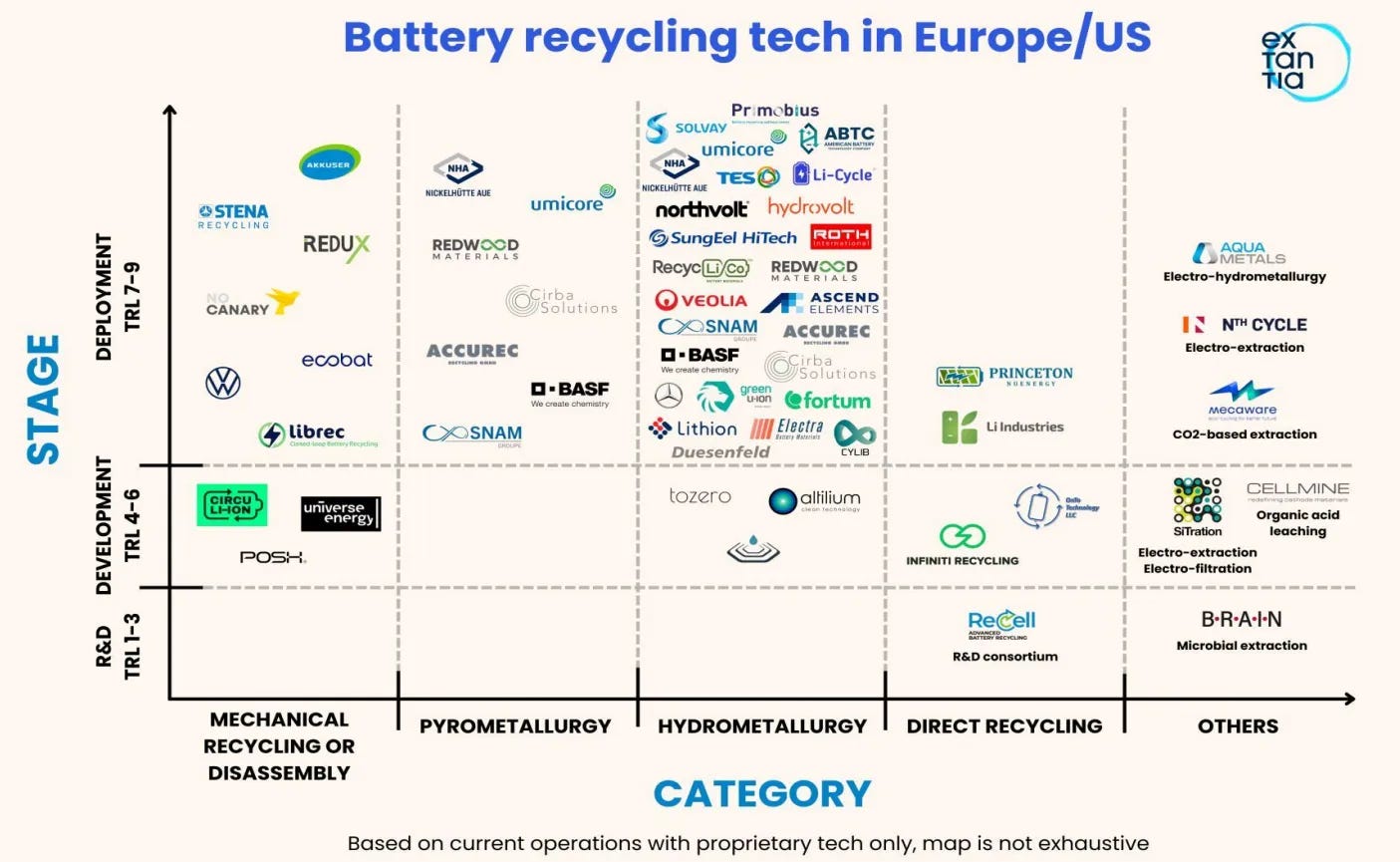
Figure 13: battery recycling tech mapping in Europe/ US [11]
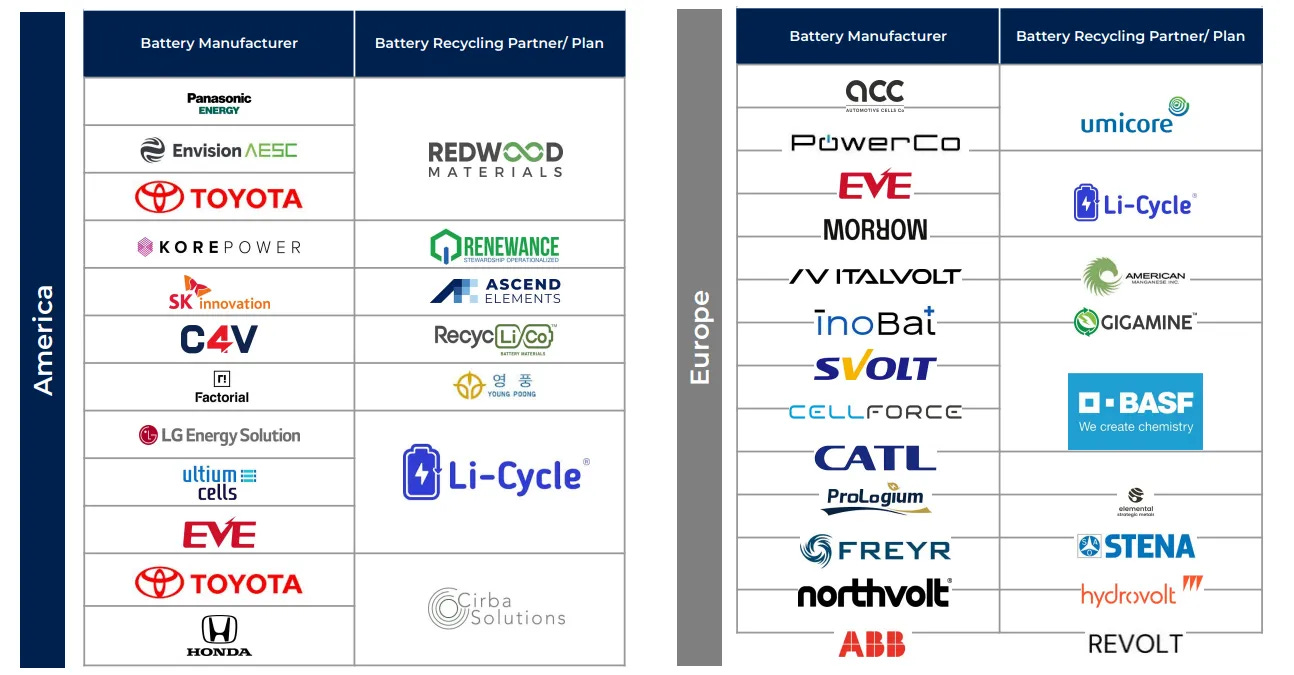
Figure 14: Gigafactories And Their Recycling Partners [11]
Key Insights
Global Battery Recycling Demand and Capacity Growth: The battery recycling market is set to expand significantly due to the rising demand for recycled materials driven by electric vehicle (EV) adoption. By 2030, planned global recycling capacity is expected to reach 1.5 million tons of battery waste annually. This growth is initially fueled by scrap from gigafactories, with end-of-life (EoL) batteries becoming a major contributor from 2030 onwards. The global volume of battery scrap is projected to increase from around 110 GWh (5.5 million tons) in 2023 to 480 GWh (24 million tons) by 2033, underscoring the need for efficient recycling infrastructure to manage this surge.
Economic and Environmental Benefits: Recycling critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel from batteries can reduce supply chain costs by 30-40% compared to primary extraction methods. Additionally, utilizing recycled materials can lower greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70%, making battery recycling a key factor in sustainable resource management.
Investments in Recycling Technologies: Significant investments are being made in recycling technologies globally. For example, Redwood Materials raised over $1 billion to enhance end-of-life battery collection and increase refining capacity. They also received a conditional commitment for a $2 billion loan from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) for battery materials made from recycled content. Similarly, Ascend Elements raised $704 million to establish a cathode precursor facility in North America using recycled materials.
Market and Policy Dynamics: The U.S. regulatory landscape for lithium battery recycling is fragmented, lacking a comprehensive federal mandate, though regulations like RCRA and HMR ensure safe handling and transportation. States like California lead with strict recycling laws, such as the Universal Waste Rule and AB 2440, mandating collection and recycling programs. Federal and state incentives, including tax credits and grants, support infrastructure development, but the overall approach remains uneven, highlighting the need for more cohesive national policies to enhance recycling rates and sustainability.